Budgeting is essential for attaining economic balance and freedom. However, with so many techniques obtainable, it may be overwhelming to pick one that works first-rate for you. One of the most popular and powerful techniques is the “Golden Rule for Budgeting,” frequently known as the “50/30/20” rule. In this article, we will explore this rule in detail, explain the way to put it into force, and provide tips for overcoming commonplace demanding situations. Let’s dive into the arena of budgeting and find out how the Golden Rule assists you in manipulating your budget more correctly.
Introduction to Budgeting
Definition and Importance of Budgeting
Budgeting is the manner of making a plan to spend your money. This spending plan, additionally called finances, enables you to determine in advance whether you have enough cash to do the stuff you need to do or would love to do. Without a price range, you might run the danger of spending more than you earn or no longer saving enough for future wishes.
Budgeting is crucial because it:
- Controls Spending: Helps you keep your spending in check.
- Ensures Savings: Encourages you to save for future goals.
- Reduces Stress: Alleviates financial worries by planning.
- Improves Financial Health: This leads to better overall financial well-being.
Understanding the Golden Rule
Explanation of the “50/30/20” Rule
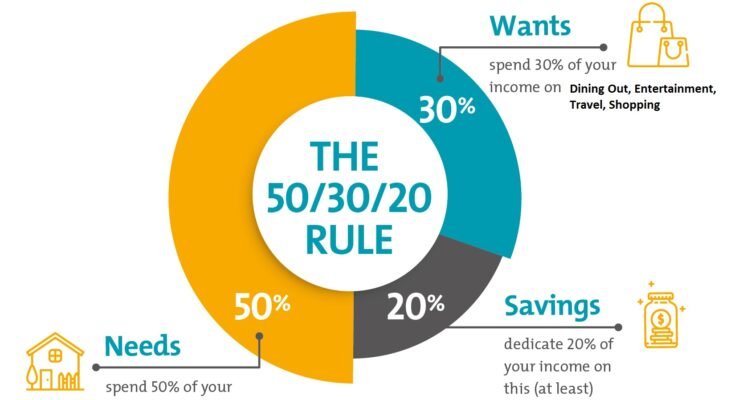
The Golden Rule for Budgeting, or the “50/30/20” rule, is a simple approach to managing your finances. This regulation classifies your after-tax income into three categories:
- 50% for Needs: Essential expenses that you must pay.
- 30% for Wants: Non-essential expenses that you enjoy.
- 20% for Savings and Debt Repayment: Money set aside for savings and paying off debts.
Origin and Purpose of the Rule
The 50/30/20 rule was popularized with the aid of Senator Elizabeth Warren & her daughter Amelia Warren Tyagi in their e-book, “All Your Worth: The Ultimate Lifetime Money Plan.” The reason for the guideline is to provide an easy framework for budgeting that all of us can observe, irrespective of our monetary expertise or earnings degree. It’s designed to help you strike a stability between spending on necessities, enjoying lifestyles, and securing your monetary future.
Must Read: What is Master Budget?
Detailed Breakdown
50%: Needs
Needs are essential expenses that you cannot avoid. These include:
- Housing: This covers your hire or mortgage bills, ensuring you have got a place to live.
- Utilities: Essential offerings together with electricity, water, heating, and internet fall under this category.
- Groceries: This includes primary food and household substances necessary for everyday living.
- Transportation: Whether it’s vehicle bills, fuel, or public transit charges, transportation expenses are critical for commuting and daily activities.
- Insurance: Health, automobile, and home coverage are vital to shield against unexpected events and liabilities.
- Minimum Debt Payments: These are the minimal required bills on loans and credit score playing cards to keep away from consequences and maintain correct credit.
Prioritizing those essential prices ensures that your simple wishes are met, imparting stability and peace of mind. If your desires exceed 50% of your profits, it’s important to assess and regulate your spending.
Strategies to Manage Needs Over 50%
- Reduce Costs: Look for approaches to lower your expenses. This might consist of moving to a less costly domestic, reducing application usage, or locating less expensive grocery alternatives.
- Increase Income: Consider taking up additional work, looking for a boost, or exploring aspect hustles to reinforce your profits.
- Budget Review: Regularly review your budget to identify regions wherein you may reduce lower back and reallocate the price range to crucial wishes.
By maintaining wishes within 50% of your profits, you keep balanced finances that permit savings and discretionary spending, fostering financial fitness and resilience.
30%: Wants
Wants are non-crucial prices that, whilst not vital to your survival or fundamental well-being, notably decorate your way of life and typical happiness. These are the discretionary spending areas that permit you to experience life and take pleasure in pleasures. Some not-unusual examples include:
- Dining Out: Expenses at eating places, takeout food, and espresso stores. This class covers the entirety from speedy food to excellent dining.
- Entertainment: Costs related to movies, concert events, pastimes, subscriptions (like Netflix or Spotify), and different amusement sports.
- Travel: Spending on holidays, weekend getaways, and day journeys, consisting of transportation, accommodation, and activities.
- Shopping: Purchases of clothing, electronics, gadgets, and different gadgets that aren’t strictly vital but bring joy and comfort.
While it’s essential to bask in wants to maintain a balanced and pleasurable lifestyle, it’s similarly crucial to maintain these prices within 30% of your after-tax income. This tenet allows make certain that you experience your money without overspending on non-essentials. Overspending in this class can cause monetary stress and decrease the funds available for vital charges and financial savings.
Sticking to the 30% rule calls for conscious spending decisions and prioritizing what brings you the maximum joy and price. For example, in case you love traveling, you would possibly choose to spend extra on trips and cut lower back on dining out or entertainment subscriptions. Budgeting apps and tracking equipment will let you screen your spending in this category, making it easier to stay in the allotted percentage.
By managing your wants wisely, you can keep a snug way of life whilst making sure that your financial health stays robust. This balance between entertainment and duty is the key to a sista.
20%: Savings and Debt Repayment
Allocating 20% of your income to financial savings and debt reimbursement is important for securing your monetary future. This part of your finances guarantees you are organized for surprising expenses and future desires and decreases financial stress.
- Emergency Fund: Start by way of building an emergency fund. This fund has to cover three months’ well worth of dwelling expenses. It’s a financial safety net for unexpected activities like medical emergencies, car maintenance, or process loss. Having an emergency fund prevents you from counting on credit playing cards or loans in a disaster, averting similar debt.
- Retirement Savings: Next, consciousness of your retirement financial savings. Contribute regularly to retirement money owed like a 401(ok) or IRA. These debts offer tax benefits and compound hobbies, helping your financial savings develop over time. The in advance you begin saving for retirement, the more time your cash has to develop, ensuring a snug future.
- Debt Repayment: Paying off debt past the minimal payments is critical. High-interest debt, like credit card balances and personal loans, can speedily acquire and grow to be overwhelming. Prioritize paying off these debts to save on interest and reduce monetary pressure. The quicker you pay off your debt, the extra cash you shop in the end.
- Investments: Consider investing in stocks, bonds, or different property. Investing allows your cash to develop and build wealth over the years. Diversifying your investments can provide stability among threats and go back, assisting you to gain your monetary dreams.
By constantly setting aside 20% of your profits for savings and debt repayment, you put together for future desires, lessen financial stress, and paint in the direction of a secure economic destiny. This disciplined approach to coping with your budget can cause extra financial stability and peace of thoughts.
5 Benefits of the Golden Rule in Budgeting
Here are five key benefits of using this budgeting method:
Simplicity and Ease of Implementation
The 50/30/20 rule is simple to apprehend. You allocate 50% of your after-tax earnings to desires, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt reimbursement. This simplicity makes it reachable to every person, irrespective of financial know-how. You don’t want to be a financial expert to observe this rule, making it a terrific starting point for budgeting novices.
Balanced Financial Approach
This rule allows you to strike stability by protecting crucial costs, playing life, and securing your monetary future. By ensuring that you allocate 50% of your profits to needs, you cover all essential fees. The 30% allotted to wishes allows for discretionary spending, preventing feelings of deprivation. The last 20% dedicated to financial savings and debt reimbursement allows the construction of a secure monetary future.
Flexibility
The 50/30/20 rule is flexible and may be adjusted to match special financial situations. For example, in case you stay in an area with a high value of residing, you would possibly need to allocate more than 50% for your wishes. Similarly, when you have widespread debt or competitive savings dreams, you can adjust the percentages to suit your priorities.
Encourages Financial Discipline
Following this rule promotes the financial area. By allocating a fixed percent of your income to savings and debt compensation, you’re continually operating closer to monetary balance. This field facilitates constructing an emergency fund, saving for retirement, and decreasing debt, which is important for long-term financial health.
Reduces Financial Stress
By imparting a clean structure in your finances, the 50/30/20 rule enables reduce monetary stress. Knowing that your crucial expenses are included and that you are saving for destiny offers peace of mind. This structure also enables you to overspend.
Step-by-Step Implementation of the Golden Rule for Budgeting
Implementing the Golden Rule for budgeting, additionally called the 50/30/20 rule, includes a clear and systematic technique for dealing with your finances. This method divides your after-tax profits into 3 categories: 50% for desires, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings and debt compensation. Here’s a step-by-step manual on how to calculate and manage your budget using this rule.
How to Calculate Your Budget
Determine Your After-Tax Income
The first step is to calculate your after-tax profits. This is the amount you take domestically despite everything taxes and deductions. For salaried personnel, that is typically located on your pay stub as the net income. For freelancers or individuals with irregular profits, you want to calculate a median monthly profit after accounting for taxes. Knowing your genuine after-tax income is vital for accurate budgeting.
Apply the 50/30/20 Rule
Once you know your after-tax income, you can divide it according to the 50/30/20 rule:
50% for Needs
Needs are essential expenses that are necessary for living and working. These include:
-
- Housing: Rent or mortgage payments.
- Utilities: Electricity, water, heating, and internet.
- Groceries: Basic food and household supplies.
- Transportation: Car payments, fuel, public transit costs.
- Insurance: Health, auto, and home insurance.
- Minimum Debt Payments: Required monthly payments on loans and credit cards. Ensure that these expenses do not exceed 50% of your after-tax income. If they do, consider finding ways to reduce costs, such as downsizing your living space or cutting back on utility usage.
30% for Wants
Wants are non-essential expenses that enhance your lifestyle. These include:
-
- Dining Out: Restaurants, takeout, and coffee shops.
- Entertainment: Movies, concerts, hobbies, and subscriptions.
- Travel: Vacations and weekend getaways.
- Shopping: Clothing, electronics, and other discretionary purchases. Keep your spending on wants within 30% of your after-tax income to maintain a balance between enjoying life and financial stability.
20% for Savings and Debt Repayment
This category is vital for building a secure financial future. It includes:
-
- Emergency Fund: Savings for unexpected expenses.
- Retirement Savings: Contributions to accounts like 401(k) or IRA.
- Debt Repayment: Paying off loans and credit card debt beyond the minimum payments.
- Investments: Investing in stocks, bonds, or other assets. Consistently allocating 20% of your income to savings and debt repayment helps prepare for future needs and reduces financial stress.
Tips for Tracking Expenses
1. Use Budgeting Apps Budgeting apps like Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), and PocketGuard can help you track your spending and ensure you stay within your budget. These apps categorize expenses automatically, making it easier to monitor where your money goes.
2. Keep a Spending Diary Write down every expense, no matter how small. Keeping a spending diary helps you become more aware of your spending habits and identify areas where you can cut back.
3. Review Monthly Statements Regularly check your bank and credit card statements to monitor your spending. This practice helps you catch any discrepancies and stay on track with your budget.
By following these steps and tips, you can effectively implement the Golden Rule for budgeting, ensuring a balanced approach to managing your finances. This method not only helps you cover your essential needs but also allows for discretionary spending and future financial security.
Adjusting the Rule for Personal Needs
Customizing Percentages Based on Personal Circumstances
While the 50/30/20 rule is a great starting point, it might need adjustments based on your situation. For instance:
- High Cost of Living: If you live in an expensive area, you might allocate more than 50% for your needs.
- Aggressive Savings Goals: If you’re saving for a big goal, you might increase the savings percentage.
- Debt Repayment Focus: If you have significant debt, you might allocate more than 20% to debt repayment.
Examples of Adjusted Budgets
- High Cost of Living: 60% needs, 20% wants, 20% savings/debt.
- Aggressive Savings: 50% needs, 20% wants, 30% savings/debt.
- Debt Repayment: 50% needs, 25% wants, 25% savings/debt.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Dealing with Irregular Income
If you have an irregular income, such as freelancing or commission-based work, budgeting can be tricky. Here are some tips:
- Create a Baseline Budget: Base your budget on your lowest expected income.
- Save During High-Income Months: Put extra money into savings during high-earning months to cover lean periods.
- Use a Three-Month Average: Calculate your average income over three months to get a more stable figure for budgeting.
Managing Unexpected Expenses
Unexpected expenses can derail your budget. Here are some strategies to handle them:
- Create an Emergency Fund: Aim to save 3-6 months of spending.
- Review and Adjust Your Budget: If an unexpected expense arises, temporarily cut back on wants to cover it.
- Stay Flexible: Be willing to adjust your budget as needed to accommodate unexpected costs.
Tools and Resources
Recommended Budgeting Apps and Tools
- Mint: Tracks your spending, creates budgets, and offers monetary advice.
- YNAB (You Need A Budget): Focuses on proactive budgeting and allows you to shop.
- PocketGuard: Shows how a good deal disposable profits you have got after payments and financial savings.
- Goodbudget: Envelope budgeting method for coping with prices.
Useful Financial Planning Resources
- Books: “All Your Worth: The Ultimate Lifetime Money Plan” by way of Elizabeth Warren and Amelia Warren Tyagi.
- Websites: Financial blogs like The Simple Dollar, NerdWallet, and Budget Bytes.
- Podcasts: “The Dave Ramsey Show,” “Freakonomics Radio,” and “The Money Guy Show.”
Case Studies
Real-Life Examples of Successful Budgeting
- Young Professional: John, a 28-year-old software program engineer, uses the 50/30/20 rule to keep a down payment on a residence. By sticking to his budget, he’s controlled to shop 20% of his profits each month and is on the right track to buy his first home in two years.
- Family with Kids: Sarah and Mark, a married couple with kids, have custom-designed the guideline to 60/20/20 because of better housing expenses. Despite the adjustment, they have efficaciously built an emergency fund and are paying off student loans quicker than anticipated.
Interviews with Financial Experts
-
Financial Advisor’s Perspective: Interview a monetary consultant about the benefits and boundaries of the 50/30/20 rule.
-
Budgeting Coach’s Tips: Speak with a budgeting educator about a way to stay encouraged and constant with budgeting.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
- The Golden Rule for Budgeting (50/30/20) is an easy and powerful way to manage your budget.
- Allocating 50% for desires, 30% for wishes, and 20% for financial savings and debt compensation allows you to reap economic stability.
- Customizing the rule to fit your occasions could make it even greater powerful.
- Tools, resources, and expert recommendations will let you stay on track and conquer challenges.
Encouragement to Start Budgeting Today
Budgeting may additionally appear daunting, but with the Golden Rule for Budgeting, it’s less difficult than you observed. Start small, be consistent, and you may see the benefits very quickly. Remember, the important thing to monetary success is not how much you are making, but the way you manage it.