How do financial markets work? Financial markets are dynamic ecosystems in which various entities change financial belongings like stocks, bonds, and currencies. These markets facilitate capital elevating, investment opportunities, and risk control for agencies and people. Key gamers consist of investors, traders, and financial establishments who buy and sell belongings based on supply, demand, financial information, and investor sentiment. Stock markets just like the New York Stock Exchange showcase ownership in groups, whilst bond markets offer debt units. Foreign exchange markets cope with currency trading. Overall, monetary markets drive economic growth, innovation, and development by allocating capital efficaciously.
How Do Financial Markets Work?
Financial Markets and Their Importance
Financial markets are essential systems wherein buyers and sellers interact in trading economic property together with stocks, bonds, currencies, and derivatives. These markets facilitate the elevating of capital, transfer of threat, and worldwide trade, playing a critical role in the usual monetary balance and boom. They provide liquidity, allowing agencies to develop and clients to invest, making sure green allocation of assets across the financial system.
Different Types of Financial Markets
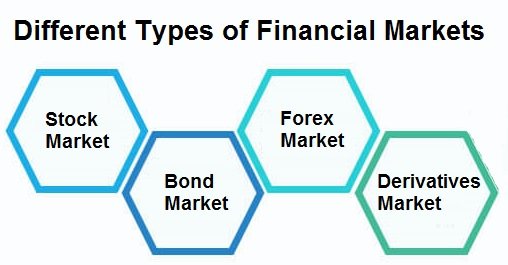
Stock Market
The inventory marketplace is in which shares of publicly held businesses are traded. It permits agencies to elevate price range with the aid of issuing stocks and offers traders with possibility to personal part of the organization and earn returns through dividends and capital profits.
Bond Market
The bond marketplace includes the buying and selling of debt securities, usually bonds. A bond is a hard and fast-income funding where an investor loans cash to an entity (company or governmental) that borrows the funds for a described length at a variable or constant interest charge.
Forex Market
The foreign exchange (foreign exchange) marketplace is a global market for exchanging country-wide currencies in opposition to each other. It is the most important monetary market in the world and is important for conducting worldwide exchange and investment.
Derivatives Market
The derivatives marketplace offers financial contracts whose fee is derived from the performance of property together with shares, bonds, currencies, interest costs, or market indexes. Common derivatives consist of futures, alternatives, and swaps, used for hedging and hypothesis.
Must Read: Swing Trading Techniques Best Guide For Beginners
Types of Financial Markets
Primary Markets
In the number one market, new securities are issued and bought without delay by traders. Companies and governments use this marketplace to elevate new capital. For instance, an Initial Public Offering (IPO) is when an agency sells its stocks to the public for the first time.
Secondary Markets
The secondary market is where previously issued securities are traded among traders. This consists of inventory exchanges just like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ. The secondary market gives liquidity and enables buyers to buy and promote securities.
Money Markets vs. Capital Markets
Money Markets
Involve trading short-term debt securities with maturities of one year or less. These include Treasury bills, commercial paper, & certificates of deposit. Participants use money markets for borrowing and lending in the short term.
Capital Markets
Capital markets trade longer-term securities with maturities greater than one year. This includes stocks and bonds. Capital markets are essential for raising long-term funds for companies and governments.
Key Players in Financial Markets
Roles of Investors, Brokers, Market Makers, and Regulators
Investors
Individuals or institutions who invest money expect to make a profit. They can be retail investors (individuals) or institutional investors (pension funds, mutual funds, etc.).
Brokers
Brokers act as intermediaries between buyers & sellers of securities. They facilitate transactions and provide market information and analysis to investors.
Market Makers
Market makers provide liquidity to the market by being ready to buy and sell securities at any time. They profit from the bid-ask spread and ensure that trades can be executed smoothly.
Regulators
Regulators oversee financial markets to ensure equity, transparency, and efficiency. They implement policies and policies to guard traders and hold market integrity. Examples encompass the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) within the U.S. And the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) within the U.K.
How These Players Interact Within the Market
In monetary markets, unique human beings work together to keep things walking easily. Investors determine where to make investments by way of using data from brokers. Brokers help join buyers with sellers, and marketplace makers ensure there may be enough cash to be had for these transactions to manifest. Regulators watch over all of us to make sure they follow the guidelines, preserving investors’ security and the marketplace’s stability.
Mechanisms of Financial Markets
How Trades Are Executed (Buying and Selling Securities)
Trades in financial markets are accomplished through diverse mechanisms, which include exchanges and over-the-counter (OTC) markets. In trade, customers and dealers meet in a centralized area (physical or digital) to change securities. The buying and selling technique involves matching buy and sell orders primarily based on fee and time precedence.
Order Types and How They Impact Transactions
Market Orders
A market order is a request to purchase or sell securities promptly at the best available price. Market orders ensure quick execution but may not guarantee the price.
Limit Orders
A limit order specifies the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay or the minimum price a seller is willing to accept. Limit orders ensure price control but may not be executed if the market price does not reach the specified limit.
Stop Orders
When the set stop price is reached, the stop order converts into a market order. It is used to limit losses or protect profits in a position.
Stop-Limit Orders
A stop-limit order combines the characteristics of stop & limit orders. Once the stop price is reached, the order becomes a limit order to buy or sell at a specified price.
Stock Market Basics
What Stocks Are and How They Are Traded
Stocks represent ownership in a company and entitle the shareholder to a portion of the company’s profits and assets. Stocks are traded on stock exchanges, where buyers and sellers meet to transact shares. The stock market provides a platform for companies to raise capital by issuing shares to the public and for investors to buy and sell shares to achieve their financial goals.
How Stock Prices Are Determined
Stock fees are decided by delivery and call for within the marketplace. Factors influencing inventory expenses consist of the agency’s overall performance, enterprise trends, financial situations, and investor sentiment. Stock costs can vary due to modifications in those elements, and the market’s belief in a company’s potentialities plays an important position in figuring out its inventory charge.
Bond Market Essentials
What Bonds Are and Their Purpose
Bonds are debt securities issued via businesses, governments, or other entities to elevate capital. When an investor buys a bond, they’re lending money to the company in trade for periodic hobby bills and the return of the bond’s face value at maturity. Bonds provide a predictable income movement and are considered less risky than shares.
How Bond Prices and Yields Are Determined
Think of bond fees like a seesaw. They pass up and down based totally on a few things: how great deal hobby rates are, how trustworthy the borrower is, and how lengthy you need to wait to get your cashback. If interest fees cross up, bond charges go down, and the alternative manner round. You get the yield again from owning a bond, including the interest you receive and any additional money you earn or lose. To calculate the yield to maturity, determine how much you’ll earn by holding onto the bond until it matures.
Foreign Exchange (Forex) Market
Currency Trading and Its Global Impact
The foreign exchange marketplace is like a large shop wherein human beings alternate one-of-a-kind currencies. It stays open 24 hours an afternoon, 5 days a week, making it the largest and busiest cash marketplace globally. Currency buying and selling is brilliantly important for worldwide enterprises because it enables businesses to alternate one currency into another. Besides that, the forex market shall we human beings wager and protect themselves against modifications in forex fees.
How Exchange Rates Are Determined
The foreign exchange marketplace determines exchange prices based on the supply and demand for currencies. Factors influencing alternate fees encompass hobby charges, inflation, political balance, monetary overall performance, and marketplace hypothesis. Central banks also can impact change costs through monetary coverage and intervention in the foreign exchange marketplace.
Derivatives Market
Derivatives are unique agreements in finance that serve various purposes.
They are used both for hedging and speculation. They get their cost from different such things as shares, bonds, cash, or goods. People use derivatives to be safe (it is hedging) while prices of these things would possibly alternate. They also use them to bet (it is a hypothesis) and make cash when they assume charges will go up or down.
Common Derivatives Like Futures and Options
Futures
Futures contracts bind the buyer and seller to trade an asset at a set price and date later on. They’re popular for commodities, currencies, and financial instruments.
Options
Options contracts provide the client the proper, but not the responsibility, to shop for or sell an asset at a detailed rate before a positive date. There are two options: call options (proper to shop for) and put alternatives (right to promote).
Also Read: Best Online Trading Site For Beginners
Market Indices and Benchmarks
What Market Indices Are and How They Are Used
Market indices are statistical measures that music the overall performance of a specific organization of assets. They gauge the general overall performance of economic markets and serve as benchmarks for investment portfolios. The criteria on which indices are built are determined by market capitalization, area, or geographic location.
Major indices such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones, & NASDAQ
- S&P 500: The index follows the performance of 500 large-cap US stocks. companies and is widely regarded as a leading indicator of U.S. equity market performance.
- Dow Jones: The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) consists of 30 large, publicly-owned U.S. companies and is one of the oldest and most recognized stock indices.
- NASDAQ: The NASDAQ Composite Index includes over 3,000 stocks listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange, with a focus on technology and growth companies.
Market Regulations and Oversight
The Role of Regulatory Bodies
Financial markets operate below strict regulations to ensure fairness, transparency, and efficiency. Regulatory bodies just as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) play vital roles. These entities create and put into effect rules to guard investors, preserve orderly markets, and sell capital formation. For example, the SEC requires organizations to report normal economic statements, making sure that buyers have get entry to to important statistics for making knowledgeable choices.
Importance of Market Regulations
Market regulations are important for stopping fraud and malpractices. They assist in maintaining investor confidence using making sure that all market individuals observe identical regulations. Regulations additionally mitigate systemic dangers that could cause economic crises. For instance, guidelines on margin trading assist save you from excessive borrowing that would destabilize the market.
Impact of Economic Indicators
How Economic Indicators Affect Financial Markets
Economic indicators which include Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation, and unemployment fees significantly have an impact on financial markets. These signs provide insights into the fitness of an economic system and manual investor expectations.
- GDP: A developing GDP often leads to bullish markets as it shows a sturdy economic system.
- Inflation: Generally, people see moderate inflation as a sign of healthy demand, but excessive inflation can erode buying power and lead to higher interest rates, negatively impacting markets.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment can signal financial problems, main to bearish market conditions, even as low unemployment suggests economic energy.
Key Economic Indicators to Watch
Investors closely monitor various indicators, including:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): This assesses how prices of things we buy regularly, like food and clothes, are converting. It facilitates us to see if matters are becoming greater steeply priced (inflation).
- Producer Price Index (PPI): This seems at how tons money manufacturers get for what they make. If this is going up, it could imply charges may move up for us too (client inflation).
- Non-Farm Payrolls: The financial system tells us how many new jobs are being created or lost, excluding farming jobs. It helps us understand if extra people have become jobs or if there are fewer jobs available.
Market Sentiment and Behavioral Finance
Understanding Market Sentiment
Market sentiment refers to investors’ overall attitudes toward a certain asset or the market as a whole. Emotions and perceptions often drive it rather than fundamental analysis. Positive sentiment can drive prices higher, while negative sentiment can lead to declines.
Impact of Market Sentiment on Trading
Investor feelings could make things show up simply due to the fact they think they may. Let’s say investors feel like the market will pass up, so they purchase shares, which makes fees cross up. But if they suppose it’s going to move down, they promote it, and that makes fees drop. We see this a lot all through large marketplace booms and crashes.
Behavioral Finance
Behavioral finance looks at how psychological factors influence investor behavior. Common biases include:
- Overconfidence: Sometimes, investors assume they realize plenty and may do something inside the marketplace so they take big risks.
- Herding: Instead of thinking for themselves, a few traders just copy what absolutely everyone else is doing.
- Loss Aversion: When humans lose money, it hurts plenty more than after they make cash, which may cause them to make awful selections.
Technological Advancements in Trading
Role of Technology in Modern Trading
Technology has modified how buying and selling works, making it faster, smoother, and easier to do. Algorithmic trading is a big part of this transformation, using laptop packages to alternate is certainly speedy. High-frequency trading (HFT) is when plenty of trades take place in only a 2nd, aiming to make cash from small fee variations.
Impact on Market Accessibility and Efficiency
Technological development has made trading accessible to everyone, not simply huge buyers. Now, online systems and cell apps permit normal human beings to alternate too. This equipment offers marketplace data, analysis, and speedy execution. Plus, AI enables selections, making trading smoother and markets more green normal.
Global Financial Markets
Overview of Major Global Financial Markets
Financial markets operate globally, with major exchanges including:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): The most valuable stock exchange in the world.
- London Stock Exchange (LSE): A leading global exchange, known for its diverse international listings.
- Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE): Asia’s largest stock exchange, featuring major Japanese corporations.
Interconnectedness of Global Markets
The highly interconnected global financial markets. Events in one market can ripple across others due to economic linkages and investor behavior. For example, a financial crisis in one country can lead to a global sell-off as investors seek safer assets. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of international cooperation & regulation.
Historical Market Events
Significant Historical Events Shaping Financial Markets
Several historical events have profoundly impacted financial markets:
- Great Depression (1929): Triggered by a stock market crash, leading to widespread economic hardship and significant regulatory reforms.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: Sparked by the collapse of the housing bubble and Lehman Brothers’ bankruptcy, leading to a severe global recession and reforms in financial regulation.
Lessons Learned
These occasions highlight the significance of regulatory oversight, change control, and the need for investor vigilance. They also underscore the interconnectedness of world monetary structures and the capability for systemic hazard.
Personal Investment Strategies
Developing Personal Investment Strategies
Successfully investing requires a proper strategy. Key concerns include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various asset training to reduce risk.
- Risk Tolerance: Understanding private risk tolerance and selecting investments for that reason.
- Investment Goals: Defining clean targets, whether for retirement, schooling, or wealth accumulation.
Importance of Diversification and Risk Management
Diversification helps mitigate dangers by ensuring that losses in one funding no longer significantly affect the overall portfolio. Risk control includes regularly reviewing and adjusting investments to align with changing goals and marketplace conditions.
Future Trends in Financial Markets
Emerging Trends and Future Developments
Technological advancements and evolving investor needs are likely to shape the future of financial markets.
Key trends include:
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: These technologies promise to revolutionize transactions and asset possession, imparting greater transparency and protection.
- Sustainable Investing: Growing hobby in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) elements drives demand for investments that align with moral values.
- Artificial Intelligence and Big Data: AI and massive records analytics are enhancing choice-making strategies, allowing extra accurate market predictions and personalized funding strategies.
Potential Impact of Innovations
Innovations like blockchain may want to cause extra green, secure, and transparent markets. Cryptocurrencies would possibly grow to be greater mainstream, providing new investment opportunities. AI and big facts will in all likelihood continue to convert trading and funding techniques, making markets extra responsive and green.
Conclusion
Financial markets are like large, crucial engines within the international cash gadget. They assist make sure money is going in which it’s wanted, and plenty of different people and groups are worried, like ordinary human beings and large organizations. Knowing how those markets work and keeping an eye fixed on things like how the economy is doing allows all of us to make smart decisions about our money. Using new generations and clever cash plans helps people do well in those markets. And because matters change all the time, staying updated on what’s new and exciting is superbly vital to doing well.
FAQs
Q1. What are financial markets and how do they work?
Financial Markets encompass any place or gadget that provides buyers and sellers the means to alternate monetary instruments, which include bonds, equities, numerous worldwide currencies, and derivatives. Financial markets facilitate the interplay between those who want capital with the ones who have capital to invest.
Q2. What are the four types of financial markets?
Types of Financial Markets
- Stock marketplace. The stock marketplace trades shares of possession of public organizations.
- Bond market. The bond market gives opportunities for agencies and authorities to secure cash to finance a mission or investment.
- Commodities market.
- Derivatives marketplace.
Q3. How do money markets work?
Money marketplace money owed is a type of financial savings account. They pay interest, however, a few issuers provide account holders confined rights to every so often withdraw cash or write checks against the account. (Federal policies confine withdrawals. The financial institution immediately converts it to a bank account if they pass it.)
Q4. What is the structure of the financial market?
The financial market’s shape broadly divides into Private Market and Public Market. D. The Money Market and Capital Market widely divide the financial market. The money marketplace caters to short-term fund necessities, whilst the capital marketplace takes care of long-term funding desires.
Q5. How do you invest?
First, open a funding account based totally on whether or not you are investing for retirement, schooling, a child, or any other purpose. Select investments-including shares, bonds, finances or actual estate-that match your chance tolerance. Minimize your exposure to chance by spreading your cash across quite several asset training.