Stock marketplace volatility refers to the fast and unpredictable fee fluctuations that arise in economic markets. Understanding this concept is vital for traders and traders as it affects investment strategies and choice-making tactics. This article will explore various “Stock market volatility strategies” to assist navigate these turbulent waters.
Stock Market Volatility Strategies
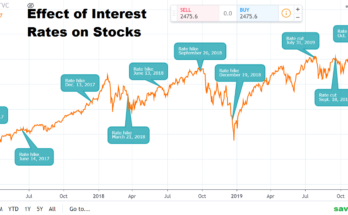
Causes of Market Volatility
Economic Indicators and Events
- Economic reviews provide data on a rustic’s economic health.
- Examples consist of GDP growth charges, employment figures, and inflation prices.
- Positive or terrible surprises in these reviews can reason large market actions.
- For example, a lower-than-predicted GDP boom rate may lead to a promote-off in stocks.
Political Instability and Geopolitical Events
- Political activities together with elections, government policy changes, or geopolitical tensions can create uncertainty in the markets.
- Uncertainty regularly results in increased volatility as buyers react to capacity risks.
Corporate Earnings Reports
- Companies launch quarterly income reviews that detail their financial performance.
- Positive income reports can enhance stock prices as buyers anticipate a future boom.
- Conversely, disappointing earnings can cause a decline in inventory expenses.
Market Speculation and Investor Sentiment
- Investor behavior and sentiment play a huge role in market volatility.
- Speculation based totally on future market expectancies can drive fees up or down swiftly.
- Emotions like fear and greed can cause quick and significant price movements.
Measuring Volatility
To manage and use “Stock market volatility strategies,” it’s crucial to measure volatility accurately. Here are some common ways to measure volatility:
Volatility Indices:
- The VIX, also called the “fear index,” measures how much volatility investors expect in the near term. It does this by looking at the prices of S&P 500 index options.
Standard Deviation and Beta:
- The standard deviation shows how much a set of numbers varies from the average number.
- Beta compares a stock’s volatility to the overall market’s volatility. A beta higher than 1 means the stock is more volatile than the market, while a beta less than 1 means it’s less volatile.
Technical Analysis Tools:
- Bollinger Bands: These are lines plotted 2 standard deviations away from a simple moving average. They show if the market is volatile or calm.
- Average True Range (ATR): This measures market volatility by looking at the range of price movements over a set period. A higher ATR means higher volatility and a lower ATR means lower volatility.
Long-Term Investing Strategies
When handling inventory marketplace volatility, lengthy-term investors can gain from several strategies:
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: This approach includes investing a fixed amount of cash at ordinary intervals, no matter the market conditions. By spreading out your investments over time, you reduce the risk of investing a massive amount at a market top. For instance, you might invest $one hundred every month rather than $1,200 all at once. This approach allows you to buy extra shares when charges are low and fewer stocks while costs are excessive, averaging out the fee over the years.
- Diversification: The diversification approach spreads your investments across extraordinary sectors and asset lessons. This can assist reduce chance due to the fact one of a kind sectors often carry out in another way below numerous marketplace situations. For example, if the technology zone isn’t doing nicely, investments in different sectors like healthcare or utilities would possibly perform higher, balancing out your usual portfolio. By now not placing all your cash into one form of investment, you could guard yourself against huge losses if one vicinity of the marketplace declines.
Why These Strategies Work
- Reduces Risk: Both strategies help manipulate risk. Dollar-price averaging avoids the hazard of investing a huge sum at the wrong time, at the same time as diversification spreads chance throughout diverse investments.
- Emotional Control: These strategies sell area and decrease the impact of emotional choice-making. By sticking to a normal investment plan and diversifying your portfolio, you’re much less in all likelihood to make impulsive choices based on market fluctuations.
- Long-Term Growth: Over time, these techniques can lead to a consistent boom. By continuously investing and keeping a whole lot of assets, you are much more likely to benefit from the market’s long-term upward trend.
Example
Imagine you have $12,000 to make investments. Instead of putting all of it into one tech inventory, you invest $1,000 each month in a mix of shares, bonds, and mutual funds. Over time, a few investments may go up, and some may match down, however common, your varied portfolio is possible to develop step by step.
Short-Term Trading Strategies
Short-term trading in the Stock market volatility strategies designed to capitalize on quick market movements. Here are three common approaches:
- Swing Trading: This strategy focuses on conserving shares for a brief period, usually a few days to weeks. Traders intend to take advantage of predicted swings within the market, whether upward or downward. By studying trends and technical signs, they try and enter and exit positions at opportune times.
- Day Trading: Day buyers buy and promote shares on the same trading day. The goal is to profit from small rate movements by leveraging massive volumes of trades. This approach demands constant marketplace tracking and speedy decision-making competencies.
- Scalping: Scalping includes executing more than one trade all through the day to capitalize on tiny price modifications. Traders who scalp are searching for to take advantage of the bid-ask spread and market inefficiencies. Successful scalping requires a dependable buying and selling platform with low latency for quick order execution.
Options Trading Strategies
Options trading offers numerous strategies to manipulate marketplace volatility successfully:
- Long Puts and Calls: Traders can purchase a put alternative (the right to promote) or a name choice (the right to shop for) to advantage of enormous fee modifications in any direction. Puts are used whilst anticipating a price drop, at the same time as calls are for expecting charge rises.
- Covered Calls and Protective Puts: Selling included calls manner owning the underlying asset and promoting the right to buy it at a better price. This strategy generates income, specifically in solid or falling markets. Protective places involve buying placed options to hedge against potential losses in a present stock position.
- Straddles and Strangles: These strategies include buying each call and placing alternatives simultaneously. A straddle is used when waiting for a large rate flow in both directions, whilst a strangle is comparable however generally with one-of-a-kind strike prices.
- Iron Condors and Butterflies: Advanced strategies in which more than one alternatives are used to profit from low volatility. Iron condors contain selling a call unfold and a placed unfold with the same expiration, while butterflies involve buying one call (put) alternative at a lower (higher) strike rate and selling two call (put) alternatives at a higher (decrease) strike rate.
Hedging Techniques
Hedging is like having insurance to manage risks from market changes:
- Using Derivatives: Derivatives inclusive of futures and alternatives are tools that assist protect investments. For instance, if someone owns stocks, they should purchase put options. This means if the stock market drops, they could nonetheless promote at a higher rate set earlier.
- Currency and Interest Rate Hedging: Investors handling foreign cash or changing hobby rates can use strategies like foreign money futures or hobby rate swaps. These techniques reduce the effect of sudden shifts in currency values or hobby costs on investments.
Portfolio Management in Volatile Markets
Managing your investments effectively in volatile markets is vital:
- Asset Mix Adjustments: It’s essential to change the balance of shares, bonds, and coins in your portfolio based totally on how the market is behaving. This helps to govern how a whole lot of risk you are exposed to.
- Regular Rebalancing: Keeping your portfolio balanced often ensures that it remains aligned with your investment desires. This approach may not emerge with an excessive amount of 1 kind of funding, which may be unstable if that part of the market drops all at once.
- Adding Diverse Investments: Including extraordinary varieties of investments like real estate, commodities, or hedge budget can lower your portfolio’s standard America and downs. These alternatives behave differently from stocks and bonds, on the way to assist stabilize your investments.
Psychological Strategies
Dealing with the ups & downs of the Stock market volatility strategies with your emotions correctly:
- Stay Calm in Turbulent Times: When the market receives shaky, it’s important to keep your cool. Avoid making brief choices driven by fear or the preference to make a quick profit.
- Stick to Your Trading Plan: Having a clear plan for whilst to shop for and sell shares assists you to stay disciplined. This plan has to be based on your economic goals and threat tolerance, now not on emotional reactions to marketplace swings.
- Recognize Common Traps: Two commonplace emotional traps are panic selling and FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out). Panic selling takes place when people promote their investments rapidly at some point in market downturns, often locking in losses. FOMO takes place while buyers buy into growing markets out of worry of lacking capability profits, now and again at inflated costs.
- Strategies for Emotional Control: Techniques like deep breathing, taking breaks from market tracking, and seeking recommendations from economic advisors can assist in manipulating emotions at some stage in risky periods.
Technology and Tools
Technology performs an important function in improving trading and investment techniques:
- Trading Platforms and Tools: Modern buying and selling structures provide tools like actual-time statistics updates, charts, and automated buying and selling options. These tools assist investors control market volatility extra effectively with the aid of offering well-timed insights and executing trades unexpectedly.
- Real-Time Data and News: Access to actual-time facts and information is critical for making informed buying and selling selections. By staying updated on marketplace tendencies and news events as they manifest, investors can react directly to changes and opportunities inside the marketplace.
- Algorithmic Trading and High-Frequency Trading (HFT): These advanced strategies involve the use of PC algorithms to execute trades at high speeds. Algorithmic trading analyzes widespread quantities of data to become aware of buying and selling opportunities, while HFT takes gain of small charge differences in milliseconds. Both strategies leverage the era to automate and optimize buying and selling techniques.
Regulatory Considerations
Market rules are rules that control how financial markets perform. These policies are vital for handling unpredictable adjustments in market prices, called volatility.
- Market Regulations and Their Impact: Regulations like circuit breakers and trading halts are important. Circuit breakers pause trading briefly when prices swing too fast, giving buyers time to make selections without panic. Trading halts prevent buying and selling altogether in extreme conditions, stopping similar panic and stabilizing markets.
- Role of Financial Authorities: During turbulent instances, the financial government steps in to maintain order. They screen marketplace conditions closely and interfere if needed to prevent immoderate volatility. Their purpose is to reassure buyers and prevent great financial instability.
- Impact on Investor Behavior: These rules impact how investors react to market changes. Knowing that guidelines are in the region can lessen fear and encourage extra rational selection-making. It facilitates maintaining self-belief in the marketplace’s equity and balance.
Future Trends
Market regulations are regulations that manage how financial markets operate. These regulations are vital for dealing with unpredictable changes in market prices, known as volatility.
- Market Regulations and Their Impact: Regulations like circuit breakers and buying and selling halts are crucial. Circuit breakers pause buying and selling temporarily whilst fees swing too speedy, giving traders time to make choices without panic. Trading halts stop trading altogether in excessive situations, stopping similar panic and stabilizing markets.
- Role of Financial Authorities: During turbulent instances, the monetary government steps in to preserve order. They screen marketplace conditions intently and interfere if needed to prevent immoderate volatility. Their goal is to reassure buyers and prevent vast economic instability.
- Impact on Investor Behavior: These guidelines have an impact on how traders react to marketplace adjustments. Knowing that guidelines are in the region can reduce worry and inspire more rational choice-making. It allows preserve self-assurance in the market’s fairness and balance.
Conclusion
Navigating inventory market volatility calls for information, strategies, and emotional areas. Investors can efficiently manipulate risks and capitalize on opportunities in volatile markets by informing the causes and measures of volatility, making use of diverse “Stock market volatility strategies,” and leveraging technology and mental strategies.